Introduction
Have you ever needed to edit an image on your computer, but weren't quite sure how to get started? For example, suppose you were asked to edit a picture for a company newsletter or blog article. Or maybe you just wanted to touch up some vacation photos before sharing them with your friends. The truth is, almost any image can be improved by a little bit of editing.
While image editing might seem a bit complicated, you don't need to be a professional designer or photographer to learn how it works. Want proof? Take a look at the images below. We were able to make this photo look a lot better with a few simple adjustments, and they took less than five minutes to complete.

Whether you need to work with images at home or at the office, this tutorial will cover the basics you'll need to know to get started. You should be able to apply these techniques in almost any image editing software.
Once you know the fundamentals, you can check out some of our other tutorials to learn more about using specific image editing applications:
Understanding the basics
We see digital image files every day in a wide range of places. For instance, whenever you see a picture on a computer or a smartphone, you're looking at a digital image file. When you take a picture with a digital camera, you're saving it as an image file. Even the images you see offline, like those in newspapers and magazines, probably started as digital image files before they were printed.
But have you ever thought about how image files work? Here are some of the basic things you should know.
Pixels
Every digital photo is made up of pixels, often abbreviated as px. You can think of a pixel as a tiny square that uses a specific color. When you look at an image file on a computer, you're really looking at thousands and thousands of pixels. But because each pixel is so small, you normally won't notice each of them unless youzoom in.
Dimensions
When you refer to the height and width of an image, you're talking about its dimensions. For example, if an image is 500 pixels wide and 200 pixels high, you could say that its dimensions are 500px by 200px (the width is usually listed first). Let's look at a few other examples.
The image below is 450px by 300px. Because this image is wider than it is tall, it's using a landscape orientation.

The image below is 300px by 450px. Because this image is taller than it is wide, it's using a portrait orientation.

Resolution
You can think of an image's resolution as the amount of detail contained in that image. The higher the resolution, the more quality the image will have. Resolution is especially important if you're thinking of printing or resizing an image. That's because you can generally make an image smaller without noticing much of a difference in the quality. However, making an image larger than its original size will usually result in a noticeable loss in quality.
In the example below, the smaller version still looks sharp and clear:

But if you try to make a low-resolution image any larger, it simply won't have enough detail to look good at the new size. As you can see in the example below, the resized image is blurry and doesn't have a lot of detail. You might also notice that some parts of the image look blocky, or pixelated.

So remember, you can usually make an image smaller without noticing a loss in quality, but you should avoid making an image any larger than its original size.
Image file formats
There are many different file formats images can use. It's important to understand the basics of image file formats, along with the most common ones you'll see when working with images.
File size and image compression
Digital image files can be very large and take up a lot of hard-drive space. Because of this, many file formats use compression in order to reduce the file size. There are two main types of file compression:
- Lossy: This compression type removes some information from the image and lowers the overall qualityin order to reduce the file size.
- Lossless: This compression type does not remove any information from the image, but it usually cannot reduce the file size as much as lossy compression.
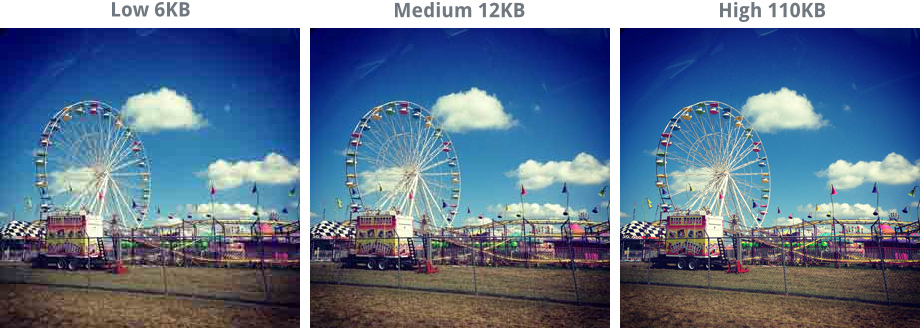
Images that use lossy compression can be saved at different quality levels. The lower the quality, the smaller the file size—that's because lowering the quality also removes more information from the image. In the example below, you can see the same image saved at different quality levels:
Recommended file formats
These are the most common file formats. We recommend using them most of the time:
- JPEG: Pronounced "jay-peg", this file type is commonly used for photographs, and most digital cameras save photos in this format by default. JPEG uses lossycompression, which means it provides a reasonably high level of quality without a very large file size.
- PNG: Pronounced "ping" or "p-n-g", this file type is commonly used for graphics and illustrations, although it can also be used for photographs. PNG uses lossless compression, meaning photographs saved with this format will usually be of a higher quality than JPEG images, but the file size will be much larger.
Other common file formats
There are many other image file formats you may encounter. One common image format is GIF. Pronounced "gif" or "jif", the GIF file type was originally designed for graphics, but it's now most commonly used for simple animated images for the web. For example, the image below is an animated GIF file.

There are also some file formats that do not use compression, such as RAW and BMP. For example, some digital cameras use a RAW format to save very high-quality images. Because these formats are uncompressed, the files tend to be much larger than JPEG or PNG files.
Keeping your originals
Whenever you edit an image file, there's a chance some of the original information from the image can be lost. Also, if you edit the same file over and over again, the edited image can begin to look much worse than the original. This is called image degradation, and it's especially problematic for files that use lossy compression, such as JPEG images.
The good news is there's an easy way to avoid this problem. If you're planning on making even basic changes to an image, such as cropping or resizing, you should also keep an original, unedited version of the file. We recommend making a habit of doing this whenever you're working with image files. This way, you'll always be able to go back to the original version.
Comments
Post a Comment